- At Meta, we help real-time communication (RTC) for billions of individuals by our apps, together with Messenger, Instagram, and WhatsApp.
- We’ve seen important advantages by adopting the AV1 codec for RTC.
- Right here’s how we’re enhancing the RTC video high quality for our apps with instruments just like the AV1 codec, the challenges we face, and the way we mitigate these challenges.
The previous couple of a long time have seen super enhancements in cell phone digital camera high quality in addition to video high quality for streaming video companies. But when we take a look at real-time communication (RTC) purposes, whereas the video high quality additionally has improved over time, it has all the time lagged behind that of digital camera high quality.
Once we checked out methods to enhance video high quality for RTC throughout our household of apps, AV1 stood out as the most suitable choice. Meta has more and more adopted the AV1 codec over time as a result of it provides excessive video high quality at bitrates a lot decrease than older codecs. However, as we’ve applied AV1 for cellular RTC, we’ve additionally needed to handle quite a lot of challenges together with scaling, enhancing video high quality for low-bandwidth customers in addition to high-end networks, CPU and battery utilization, and sustaining high quality stability.
Bettering video high quality for low-bandwidth networks
This submit goes to give attention to peer-to-peer (P2P, or 1:1) calls, which contain two members.
Individuals who use our services expertise a spread of community situations – some have actually nice networks, whereas others are utilizing throttled or low-bandwidth networks.
This chart illustrates what the distribution of bandwidth appears to be like like for a few of these calls on Messenger:
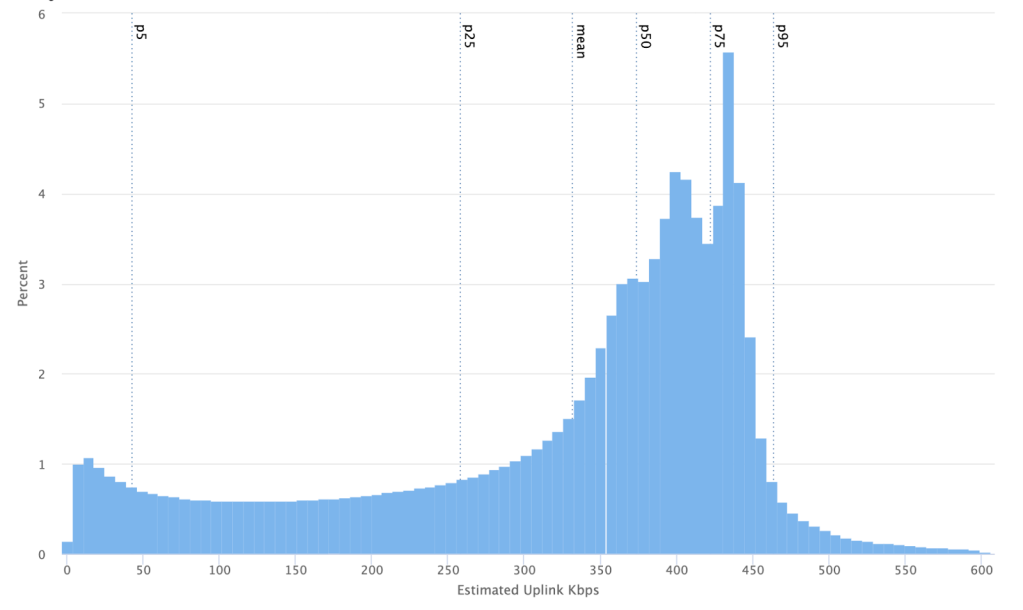
As seen in Determine 1, some calls function in very low-bandwidth situations.
We contemplate something lower than 300 Kbps to be a low-end community, however we additionally see a number of video calls working at simply 50 Kbps, and even underneath 25 Kbps.
Word that this bandwidth is the share for the video encoder. Whole bandwidth is shared with audio, RTP overhead, signaling overhead, RTX (re-transmissions of packets to deal with misplaced packets)/FEC (ahead error correction)/duplication (packet duplication), and so forth. The massive assumption right here is that the bandwidth estimator is working appropriately and estimating true bitrates.
There are not any common definitions for low, mid, and excessive networks, however for the aim of this weblog submit, lower than 300 Kbps will probably be thought of as low, 300-800 Kbps as mid, and above 800 Kbps as a excessive, HD-capable, or high-end community.
Once we appeared into enhancing the video high quality for low-bandwidth customers, there have been few key choices. Migrating to a more recent codec akin to AV1 offered the best alternative. Different choices akin to higher video scalers and region-of-interest encoding provided incremental enhancements.
Video scalers
We use WebRTC in most of our apps, however the video scalers shipped with WebRTC don’t have the very best quality video scaling. We’ve been capable of enhance the video scaling high quality considerably by leveraging in-house scalers.
At low bitrates, we regularly find yourself downscaling the video to encode at ¼ decision (assuming the digital camera seize is 640×480 or 1280×720). With our customized scaler implementations, we now have seen important enhancements in video high quality. From public assessments we noticed features in peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) by 0.75 db on common.
Here’s a snapshot exhibiting outcomes with the default libyuv scaler (a field filter):

And the outcomes after downscaling with our video scaler:

Area-of-interest encoding
Figuring out the area of curiosity (ROI) allowed us to optimize by spending extra encoder bitrate within the space that’s most necessary to a viewer (the speaker’s face in a speaking head video, for instance). Most cellular units have APIs to find the face area with out using any CPU overhead. As soon as we now have discovered the face area we will configure the encoder to spend extra bits on this necessary area and fewer on the remaining. The simplest method to do that was to have some APIs on encoders to configure the quantization parameters (QP) for ROI versus the remainder of the picture. These modifications supplied incremental enhancements within the video high quality metrics like PSNR.
Adopting the AV1 video codec
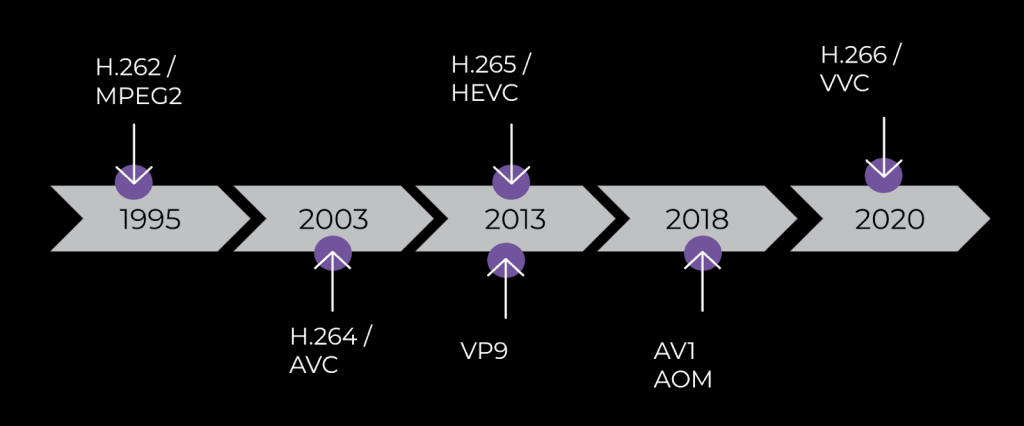
The video encoder is a key ingredient in the case of video high quality for RTC. H.264 has been the preferred codec over the past decade, with {hardware} help and most purposes supporting it. However it’s a 20-year-old codec. Again in 2018, the Alliance for Open Media (AOMedia) standardized the AV1 video codec. Since then, a number of firms together with Meta, YouTube, and Netflix have deployed it at a big scale for video streaming.
At Meta, shifting from H.264 to AV1 led us to our best enhancements in video high quality at low bitrates.
Why AV1?
We selected to make use of AV1 partly as a result of it’s royalty-free. Codec licensing (and concurrent charges) was an necessary side in our decision-making course of. Usually, if an utility makes use of a tool’s {hardware} codec, no extra codec licensing prices will probably be incurred. But when an utility is transport a software program model of the codec, there’ll almost definitely be licensing prices to cowl.
However why do we have to use software program codecs although most telephones have hardware-supported codecs?
Most cellular units have devoted {hardware} for video encoding and decoding. And today most cellular units help H.264 and even H.265s. However these encoders are designed for widespread use circumstances akin to digital camera seize, which makes use of a lot greater resolutions, body charges, and bitrates. Most cellular system {hardware} is at present able to encoding 4K 60 FPS in actual time with very low battery utilization, however the outcomes of encoding a 7 FPS, 320×180, 200 Kbps video are sometimes worse than these of software program encoders working on the identical cellular system.
The explanation for that’s prioritization of the RTC use case. Most unbiased {hardware} distributors (IHVs) are usually not conscious of the community situations the place RTC calls function; therefore, these {hardware} codecs are usually not optimized for RTC eventualities, particularly for low bitrates, resolutions, and body charges. So, we leverage software program encoders when working in these low bitrates to offer high-quality video.
And since we will’t ship software program codecs with out a license, AV1 is an excellent choice for RTC.
AV1 for RTC
The largest purpose to maneuver to a extra superior video codec is easy: The identical high quality expertise may be delivered with a a lot decrease bitrate, and we will ship a a lot higher-quality real-time calling expertise for our customers who’re on bandwidth-constrained networks.
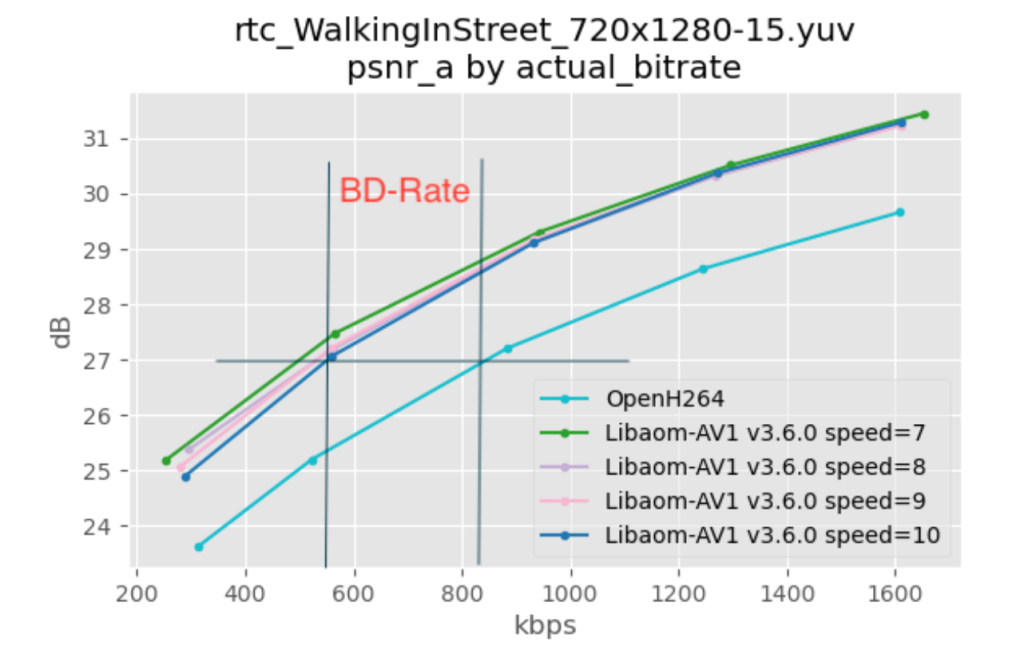
Measuring video high quality is a posh subject, however a comparatively easy method to have a look at it’s to make use of the Bjontegaard Delta-Bit Fee (BD-BR) metric. BD-BR compares how a lot bitrate varied codecs want to provide a sure high quality stage. By producing a number of samples at completely different bitrates, measuring the standard of the produced video offers a rate-distortion (RD) curve, and from the RD curve you’ll be able to derive the BD-BR (as proven under).
As may be seen in Determine 4, AV1 supplied greater high quality for all bitrate ranges in our native assessments.
Display screen-encoding instruments
AV1 additionally has a number of key instruments which are helpful for RTC. Display screen content material high quality is changing into an more and more necessary issue for Meta, with related use circumstances, together with display sharing, recreation streaming, and VR distant desktop, requiring high-quality encoding. In these areas, AV1 actually shines.
Historically, video encoders aren’t effectively suited to advanced content material akin to textual content with a number of high-frequency content material, and people are delicate to studying blurry textual content. AV1 has a set of coding instruments—palette mode and intra-block copy—that drastically enhance efficiency for display content material. Palette mode is designed in accordance with the statement that the pixel values in a screen-content body normally focus on the restricted variety of coloration values. Palette mode can symbolize the display content material effectively by signaling the colour clusters as a substitute of the quantized transform-domain coefficients. As well as, for typical display content material, repetitive patterns can normally be discovered inside the identical image. Intra-block copy facilitates block prediction inside the identical body, in order that the compression effectivity may be improved considerably. That AV1 offers these two instruments on the baseline profile is a large plus.
Reference image resampling: Fewer key frames
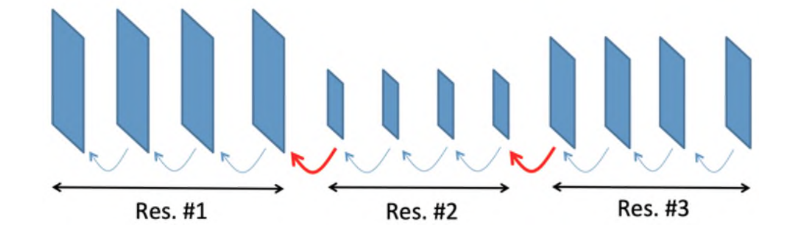
One other helpful function is reference image resampling (RPR), which permits decision modifications with out producing a key body. In video compression, a key body is one which’s encoded independently, like a nonetheless picture. It’s the one kind of body that may be decoded with out having one other body as reference.
For RTC purposes, because the bandwidth retains on altering typically, there are frequent decision modifications wanted to adapt to those community modifications. With older codecs like H.264, every of those decision modifications requires a key body that’s a lot bigger in dimension and thus inefficient for RTC apps. Such giant key frames improve the quantity of knowledge needing to be despatched over the community and lead to greater end-to-end latencies and congestion.
By utilizing RPR, we will keep away from producing any key frames.
Challenges round enhancing video high quality for low-bandwidth customers
CPU/battery utilization
AV1 is nice for coding effectivity, however codecs obtain this at the price of greater CPU and battery utilization. Plenty of trendy codecs pose these challenges when working real-time purposes on cellular platforms.
Based mostly on native lab testing, we anticipated a roughly 4 p.c improve in battery utilization, and we noticed comparable ends in public assessments. We used an influence meter to do that native battery measurement.
Although the AV1 encoder itself elevated CPU utilization three-fold when in comparison with H.264 implementation, the general contribution of CPU utilization from the encoder was a small a part of the battery utilization. The cellphone show display, networking/radio, and different processes utilizing the CPU contribute considerably to battery utilization, therefore the rise in battery utilization was 5-6 p.c (a big improve in battery utilization).
Plenty of calls run out of system battery, or folks cling up as soon as their working system signifies a low battery, so growing battery utilization isn’t worthwhile for customers except it offers elevated worth akin to video high quality enchancment. Even then it’s a trade-off between video high quality versus battery use.
We use WebRTC and Session Description Protocol (SDP) for codec negotiation, which permits us to barter a number of codecs (e.g., AV1 and H.264) up entrance after which swap the codecs with none want for signaling or a handshake throughout the name. This implies the codec swap is seamless, with out customers noticing any glitches or pauses in video.
We created a customized encoder that encapsulates each H.264 and the AV1 encoders. We name it a hybrid encoder. This allowed us to change the codec throughout the name based mostly on triggers akin to CPU utilization, battery stage, or encoding time — and to change to the extra battery-efficient H.264 encoder when wanted.
Elevated crashes and out of reminiscence errors
Even with out new leaks added, AV1 used extra reminiscence than H.264. Any time extra reminiscence is used, apps usually tend to hit out of reminiscence (OOM) crashes or hit OOM sooner due to different leaks or reminiscence calls for on the system from different apps. To mitigate this, we needed to disable AV1 on units with low reminiscence. That is one space for enchancment and for additional optimizing the encoder’s reminiscence utilization.
In-product high quality measurement
To check the standard between H.264 and AV1 utilizing public assessments, we would have liked a low-complexity metric. Metrics akin to encoded bitrates and body charges received’t present any features as the whole bandwidth accessible to ship video continues to be the identical, as these are restricted by the community capability, which implies the bitrates and body charges for video is not going to change a lot with the change within the codec. We had been utilizing composite metrics that mix the quantization parameter (QP is usually used as a proxy for video high quality, as this introduces pixel knowledge loss throughout the encoding course of), resolutions, and body charge, and freezes it to generate video composite metrics, however QP shouldn’t be comparable between AV1 and H.264 codecs, and therefore can’t be used.
PSNR is a typical metric, nevertheless it’s reference-based and therefore doesn’t work for RTC. Non-reference, video-quality metrics are fairly CPU-intensive (e.g., BRISQUE: Blind/Referenceless Picture Spatial High quality Evaluator), although we’re exploring these as effectively.
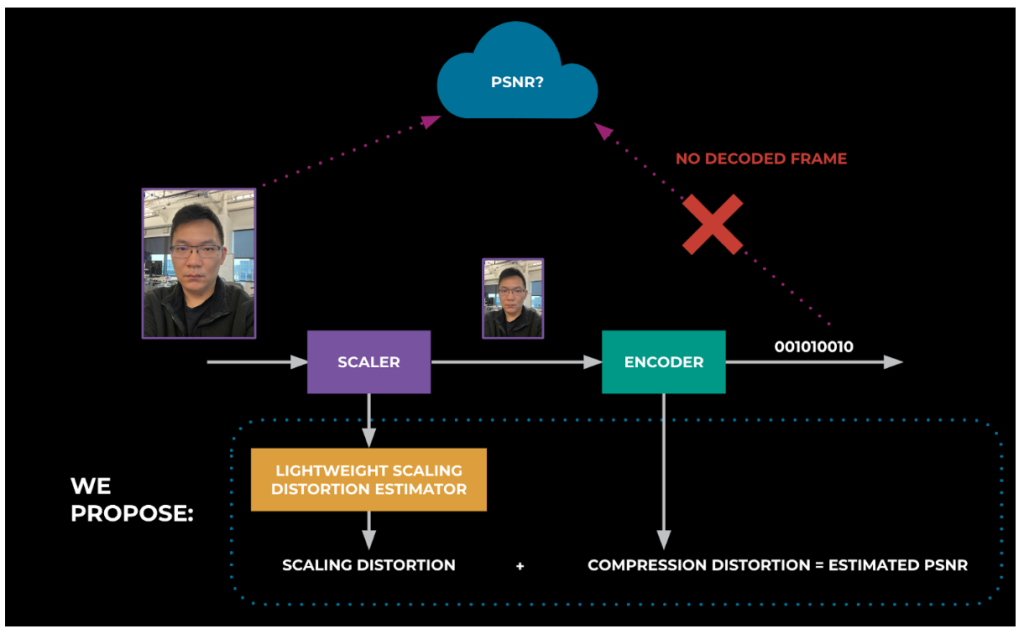
We’ve give you a framework for PSNR computation. We first modified the encoder to report distortions brought on by compression (most software program encoders have already got help for this metric). Then we designed a light-weight, scaling-distortion algorithm that estimates the distortion launched by video scaling. This algorithm can mix these scaling distortions with the encoder distortions to provide output PSNR. We developed and verified this algorithm domestically and will probably be sharing the findings in publications and at tutorial conferences over the subsequent 12 months. With this light-weight PSNR metric, we noticed 2 db enhancements with AV1 in comparison with H.264.
Challenges round enhancing video high quality for high-end networks
As a fast assessment: For our functions, excessive bandwidth covers customers for whom bandwidth is larger than 800 kbps.
Over time, there have been enormous enhancements in digital camera seize high quality. Consequently, folks’s expectations have gone up, they usually need to see RTC video high quality on par with native digital camera seize high quality.
Based mostly on native testing, we settled on settings leading to video high quality that appears much like that of digital camera recordings. We name this HD mode. We discovered that with a video codec like H.264 encoding at 3.5 Mbps and 30 frames per second, 720p decision appeared similar to native digital camera recordings. We additionally in contrast 720p to 1080p in subjective high quality assessments and located that the distinction shouldn’t be noticeable on most units aside from these with a bigger display once we performed subjective high quality assessments.
Bandwidth estimator enhancements
Bettering the video high quality for customers who’ve high-end telephones with good CPUs, good batteries, {hardware} codecs, and good community speeds appears trivial. It might seem to be all you must do is improve the utmost bitrate, seize decision, and seize body charges, and customers will ship high-quality video. However, in actuality, it’s not that straightforward.
When you improve the bitrate, you expose your bandwidth estimation and congestion detection algorithm to hit congestion extra typically, and your algorithm will probably be examined many extra instances than if you weren’t utilizing these greater bitrates.
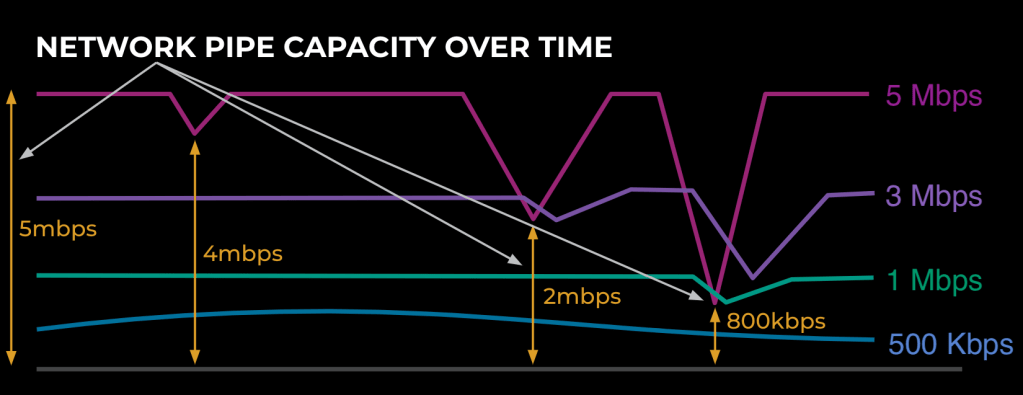
When you take a look at the community pipeline in Determine 7, the upper the bitrates you’re utilizing, the extra your algorithm/code will probably be examined for robustness over the time of the RTC name. Determine 7 reveals how utilizing 1 Mbps hits extra congestion than utilizing 500 Kbps and utilizing 3 Mbps hits extra congestion than 1 Mbps, and so forth. In case you are utilizing bandwidths decrease than the minimal throughput of the community, nevertheless, you received’t hit congestion in any respect. For instance, see the 500-Kbps name in Determine 7.
To mitigate these points, we improved congestion detection. For instance, we added customized ISP throttling detection, one thing that was not being caught by the normal delay-based estimator of WebRTC.
Bandwidth estimator and community resilience comprise a posh space on their very own, and that is the place RTC merchandise stand out. They’ve their very own customized algorithms that work finest for his or her merchandise and clients.
Secure high quality
Individuals don’t like oscillations in video high quality. These can occur once we ship high-quality video for a number of seconds after which drop again to low-quality due to congestion. Studying from previous historical past, we added help in bandwidth estimation to stop these oscillations.
Audio is extra necessary than video for RTC
When community congestion happens, all media packets may very well be misplaced. This causes video freezes and damaged audio, (aka, robotic audio). For RTC, each are dangerous, however audio high quality is extra necessary than video.
Damaged audio typically utterly prevents conversations from occurring, typically inflicting folks to hold up or redial the decision. Damaged video, then again, typically ends in much less pleasant conversations, however, relying on the state of affairs, it may be a block for some customers.
At excessive bitrates like 2.5 Mbps and better, you’ll be able to afford to have three to 5 instances extra audio packets or duplication with none noticeable degradation to video. When working in these greater bitrates with cellphone connections, we noticed extra of those congestion, packet loss, and ISP throttling points, so we needed to make modifications to our community resiliency algorithms. And since individuals are extremely delicate to knowledge utilization on their cell telephones, we disabled excessive bitrates on mobile connections.
When to allow HD?
We used ML-based focusing on to guess which name must be HD-capable. We relied on the community stats from the customers’ earlier calls to foretell if HD must be enabled or not.
Battery regressions
We’ve plenty of metrics, together with efficiency, networking, and media high quality, to trace the standard of RTC calls. Once we ran assessments for HD, we seen regressions in battery metrics. What we discovered was that almost all battery regressions don’t come from greater bitrates or decision however from the seize body charges.
To mitigate the regressions, we constructed a mechanism for detecting each caller and callee system capabilities, together with system mannequin, battery ranges, Wi-Fi or cellular utilization, and so forth. To allow high-quality modes, we test each side of the decision to make sure that they fulfill the necessities and solely then can we allow these high-quality, resource-intensive configurations.
What the long run holds for RTC
{Hardware} producers are acknowledging the numerous advantages of utilizing AV1 for RTC. The brand new Apple iPhone 15 Professional helps AV1’s {hardware} decoder, and the Google Pixel 8 helps AV1 encoding and decoding. {Hardware} codecs are an absolute necessity for high-end community and HD resolutions. Video calling is changing into as ubiquitous as conventional audio calling and we hope that as {hardware} producers acknowledge this shift, there will probably be extra alternatives for collaboration between RTC app creators and {hardware} producers to optimize encoders for these eventualities.
On the software program aspect, we are going to proceed to work on optimizing AV1 software program encoders and growing new encoder implementations. We attempt to present the most effective expertise for our customers, however on the identical time we need to let folks have full management over their RTC expertise. We are going to present controls to the customers in order that they will select whether or not they need greater high quality at the price of battery and knowledge utilization, or vice versa.
We additionally plan to work with IHVs to collaborate on {hardware} codec growth to make these codecs usable for RTC eventualities together with low-bandwidth use circumstances.
We additionally will examine forward-looking options akin to video processing to extend the decision and body charges on the receiver’s rendering stack and leveraging AI/ML to enhance bandwidth estimation (BWE) and community resiliency.
Additional, we’re investigating Pixel Codec Avatar applied sciences that may permit us to transmit the mannequin/share as soon as after which ship the geometry/vectors for receiver aspect rendering. This allows video rendering with a lot smaller bandwidth utilization than conventional video codecs for RTC eventualities.











+ There are no comments
Add yours