- We’ve partnered with Voltron Knowledge and the Arrow group to align and converge Apache Arrow with Velox, Meta’s open supply execution engine.
- Apache Arrow 15 contains three new format layouts developed by this partnership: StringView, ListView, and Run-Finish-Encoding (REE).
- This new convergence helps Meta and the bigger group construct information administration techniques which can be unified, extra environment friendly, and composable.
Meta’s Knowledge Infrastructure groups have been rethinking how information administration techniques are designed. We need to make our information administration techniques extra composable – which means that as a substitute of individually growing techniques as monoliths we determine frequent parts, issue them out as reusable libraries, and leverage frequent APIs and requirements to extend the interoperability between them.
As we decompose our giant, monolithic techniques right into a extra modular stack of reusable parts, open requirements, reminiscent of Apache Arrow, play an essential function for interoperability of those parts. To additional our efforts in making a extra unified information panorama for our techniques in addition to these within the bigger group, we’ve partnered with Voltron Knowledge and the Arrow group to converge Apache Arrow’s open supply columnar layouts with Velox, Meta’s open supply execution engine.
The end result combines the effectivity and agility supplied by Velox with the widely-used Apache customary.
Why we’d like a composable information administration system
Meta’s information engines assist large-scale workloads that embody processing giant datasets offline (ETL), interactive dashboard era, advert hoc information exploration, and stream processing. Extra just lately, a wide range of function engineering, information preprocessing, and coaching techniques had been constructed to assist our quickly increasing AI/ML infrastructure. To make sure our engineering groups can effectively keep and improve these engines as our merchandise evolve, Meta has began a collection of initiatives aimed toward growing our engineering effectivity by minimizing the duplication of labor, bettering the expertise of inside information customers by extra constant semantics throughout these engines, and, finally, accelerating the tempo of innovation in information administration.
An introduction to Velox
Velox is the primary mission in our composable information administration system program. It’s a unified execution engine, applied as a C++ library, aimed toward changing the very processing core of many of those information administration techniques – their execution engine.
Velox improves the effectivity of those techniques by offering a unified, state-of-the-art implementation of options and optimizations that had been beforehand solely accessible in particular person engines. It additionally improves the engineering effectivity of our group since these options can now be written as soon as, in a single library, and be (re-)used all over the place.
Velox is at present in numerous phases of integration in additional than 10 of Meta’s information techniques. We now have noticed 3-10x effectivity enhancements in integrations with well-known techniques within the business like Apache Spark and Presto.
We open-sourced Velox in 2022. Right this moment, it’s developed in collaboration with greater than 200 particular person contributors all over the world from greater than 20 corporations.
Open requirements and Apache Arrow
In an effort to allow interoperability with different parts, a composable information administration system has to grasp frequent storage (file) codecs, community serialization protocols, desk APIs, and have a unified manner of expressing computation. Oftentimes these parts need to instantly share in-memory datasets with one another, for instance, when transferring information throughout language boundaries (C++ to Java or Python) for environment friendly UDF assist.
Our focus is to make use of open requirements in these APIs as usually as attainable. Apache Arrow is an open supply in-memory structure customary for columnar information that has been broadly adopted within the business. In a manner, Arrow might be seen because the layer beneath Velox: Arrow describes how columnar information is represented in reminiscence; Velox offers a collection of execution and useful resource administration primitives to course of this information.
Though the Arrow format predates Velox, we made a aware design determination whereas creating Velox to increase and deviate from the Arrow format, making a structure we name Velox Vectors. The aim was to speed up the info processing operations generally present in our workloads in ways in which weren’t attainable utilizing Arrow. Velox Vectors offered the effectivity and agility we have to transfer quick, however in return created a fragmented area with restricted element interoperability.
To bridge this hole and create a extra unified information panorama for our techniques and the group, we partnered with Voltron Knowledge and the Arrow group to align and converge these two codecs. After a yr of labor, the brand new Apache Arrow launch, Apache Arrow 15.0.0, contains three new format layouts impressed by Velox Vectors: StringView, ListView, and Run-Finish-Encoding (REE).
Arrow 15 not solely allows environment friendly (zero-copy) in-memory communication throughout parts utilizing Velox and Arrow, but additionally will increase Arrow’s applicability in fashionable execution engines, unlocking a wide range of use instances throughout the business.
Particulars of the Arrow and Velox structure
Each Arrow and Velox Vectors are columnar layouts whose objective is to symbolize batches of information in reminiscence. A column is often composed of a sequential buffer the place row values are saved contiguously and an elective bitmask to symbolize the nullability/validity of every worth:
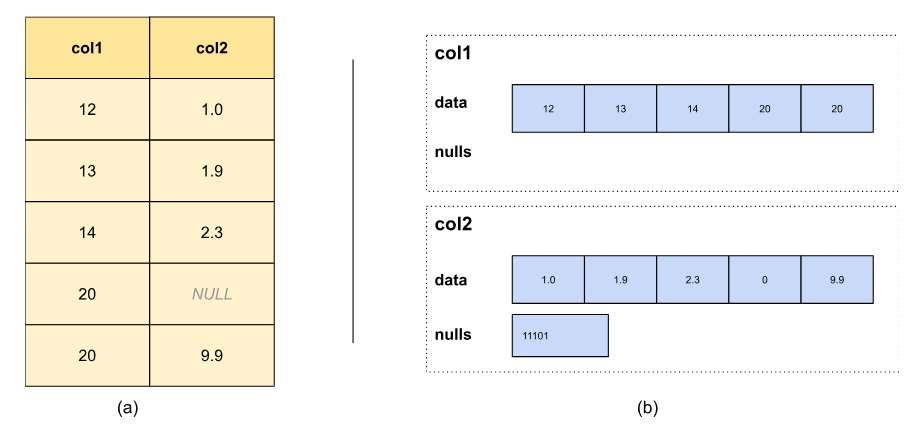
The Arrow and Velox Vectors codecs already had suitable structure representations for scalar fixed-size information sorts (reminiscent of integers, floats, and booleans) and dictionary-encoded information. Nonetheless, there have been incompatibilities in string illustration and container sorts reminiscent of arrays and maps, and an absence of assist for fixed and run-length-encoded (RLE) information.
StringView – strings
Arrow’s typical string illustration makes use of the variable-sized aspect structure, which consists of 1 contiguous buffer containing the string contents (the info), and one buffer marking the place every string begins (the offsets). The scale of a string i might be obtained by subtracting offsets[i+1] by offsets[i]. That is equal to representing strings as an array of characters:
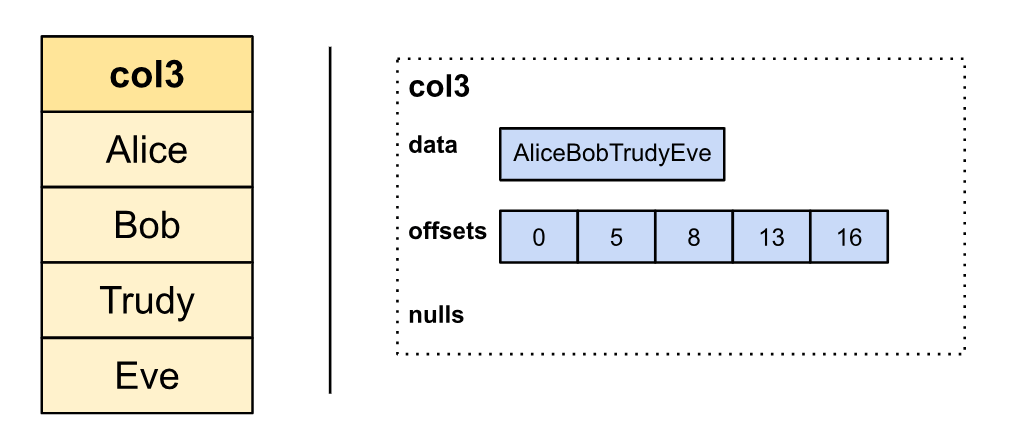
Whereas Arrow’s illustration stands out in simplicity, we discovered by a collection of experiments that the next alternate string illustration (which is now known as StringView) offers compelling properties which can be essential for environment friendly string processing:
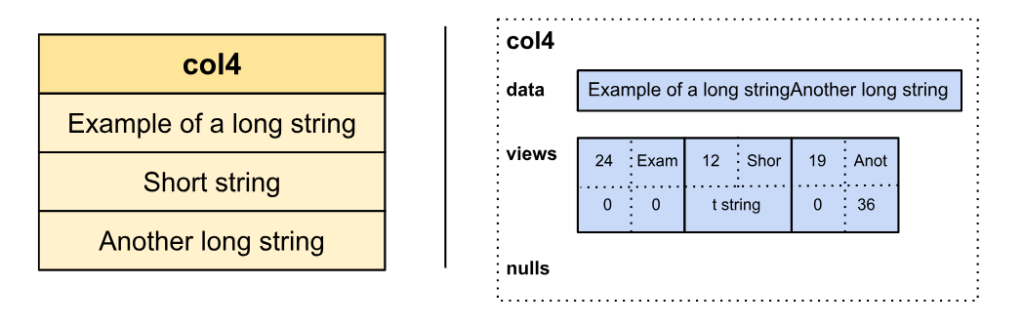
Within the new illustration, the primary 4 bytes of the view object all the time include the string measurement. If the string is brief (as much as 12 characters), the contents are saved inline within the view construction. In any other case, a prefix of the string is saved within the subsequent 4 bytes, adopted by the buffer ID (StringViews can include a number of information buffers) and the offset in that information buffer.
The advantages of this structure are:
- Small strings of as much as 12 bytes are totally inlined inside the views buffer and might be learn with out dereferencing the info buffer. This will increase reminiscence locality as the everyday cache miss of accessing the info buffer is averted, growing efficiency.
- Since StringViews retailer a small (4 bytes) prefix with the view object, string comparisons can fail-fast and, in lots of instances, keep away from accessing the info buffer. This property hurries up frequent operations reminiscent of extremely selective filters and sorting.
- StringView provides builders extra flexibility on how string information is specified by reminiscence. For instance, it permits for sure frequent string operations, reminiscent of ????() and ??????(), to be executed zero-copy by solely updating the view object.
- Since StringView’s view object has a hard and fast measurement (16 bytes), StringViews might be written out of order (e.g., first writing StringView at place 2, then 0 and 1).
Apart from these properties, now we have discovered that different fashionable processing engines and libraries like Umbra and DuckDB comply with an analogous string illustration method, and, consequently, additionally used to deviate from Arrow. In Arrow 15, StringView has been added as a supported structure and may now be used to effectively switch string batches throughout these techniques.
ListView – variable-sized containers
Variable-size containers like arrays and maps are represented in Arrow utilizing one buffer containing the flattened parts from all rows, and one offsets buffer marking the place the container on every row begins, much like the unique string illustration. The variety of parts a container on row i shops might be obtained by subtracting offsets[i+1] by offsets[i]:
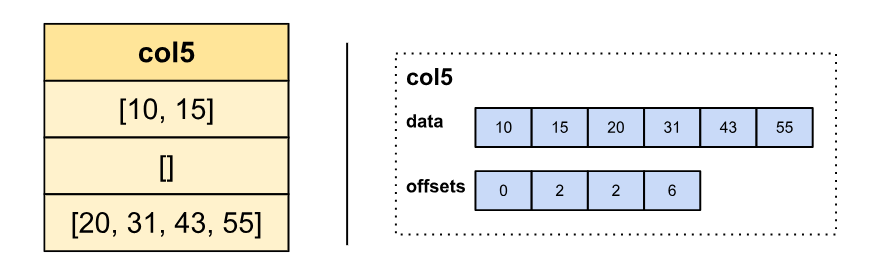
To effectively assist execution of vectorized conditionals (e.g., IF and SWITCH operations), the Velox Vectors structure has to permit builders to put in writing columns out of order. Because of this builders can, for instance, first write all even row data then all odd row data with out having to reorganize parts which have already been written.
Primitive sorts can all the time be written out of order because the aspect measurement is fixed and recognized beforehand. Likewise, strings will also be written out of order utilizing StringView as a result of the string metadata objects have a relentless measurement (16 bytes), and string contents don’t have to be written contiguously. To extend flexibility and assist out-of-order writes for the remaining variable-sized sorts in Velox, we determined to maintain each lengths and offsets buffers:
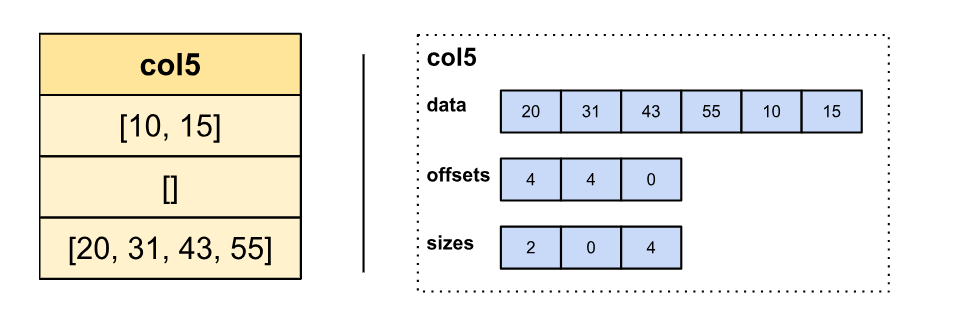
To bridge the hole, a brand new format known as ListView has been added to Arrow 15. It permits the illustration of variable-sized parts which have each lengths and offsets buffers.
Past permitting for environment friendly execution of conditionals, ListView provides builders extra flexibility to slice and rearrange containers (e.g., operations like slice() and trim_array() might be applied zero-copy), apart from permitting for containers with overlapping ranges of parts.
REE – extra encodings
We now have additionally added two extra encoding codecs generally present in information warehouse workloads into Velox: fixed encoding, to symbolize that each one values in a column are the identical, sometimes used to symbolize literals and partition keys; and RLE, to compactly symbolize consecutive runs of the identical aspect.
Upon dialogue with the group, it was determined so as to add the REE format to Arrow. The REE format is a slight variation of RLE that, as a substitute of storing the lengths of every run, shops the offset during which every run ends, offering higher random-access assist. With REEs it’s also attainable to symbolize fixed encoded values by encoding them as a single run whose measurement is the whole batch.
Composability is the way forward for information administration
Converging Arrow and Velox’s reminiscence structure is a crucial step in direction of making information administration techniques extra composable. It allows techniques to mix the ability of Velox’s state-of-the-art execution with the widespread business adoption of Arrow’s customary, leading to a extra environment friendly and seamless cooperation. The brand new extensions are already seeing adoption in libraries like PyArrow and Polars and inside Meta. Sooner or later, it’ll permit extra environment friendly interaction between initiatives like Apache Gluten (which makes use of Velox internally) and PySpark (which consumes Arrow), for instance.
We envision that fragmentation and duplication of labor might be lowered by decomposing information techniques into reusable parts that are open supply and constructed primarily based on open requirements and APIs. In the end, we hope this work will assist present the inspiration required to speed up the tempo of innovation in information administration.
Acknowledgments
This format alignment was solely attainable as a result of a broad collaboration throughout totally different teams. A particular thanks to Masha Basmanova, Orri Erling, Xiaoxuan Meng, Krishna Pai, Jimmy Lu, Kevin Wilfong, Laith Sakka, Wei He, Bikramjeet Vig, and Sridhar Anumandla from the Velox workforce at Meta; Felipe Carvalho, Ben Kietzman, Jacob Wujciak-Jens, Srikanth Nadukudy, Wes McKinney, and Keith Kraus from Voltron Knowledge; and the whole Apache Arrow group for the insightful discussions, suggestions, and receptivity to new concepts.












+ There are no comments
Add yours